You'll find all our Demetra video tutorials on this web page. Demetra is a free software package for processing spectra from the ALPY 600, LISA and eShel spectrographs from the Shelyak Instruments range. Playlist of Demetra tutorials Tutorial #1 Introduction to...
LISA Spectroscope (VIS)
4 746,00 € incl. VAT - 3 955,00 € excl. VAT
The LISA is the most sensitive instrument in our product range. Thanks to its internal reducer and low resolution, it is the undisputed master of faint objects such as novae & supernovae, planetary nebulae, comets, symbiotic stars, cataclysmic variables, galaxies…
Complete your LISA spectroscope with the products below:
Additional modules
Additional modules: technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Acc. type |
Included |
Comment |
LISA internal guiding module |
Guiding module |
Built-in LISA |
||
Internal LISA calibration module |
SE0103 |
Calibration module |
Includes Ar-Ne calibration lamp and flat lamp (tungsten) |
Grating module
Grating module : technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Included |
R @650 nm |
Dispersion (nm/mm) |
Blaze |
Grating LISA 300 t/mm |
1000 |
500 nm |
Slits
Slits : technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Included |
Material (% reflexion) |
Mirror size |
AR coating |
Comment |
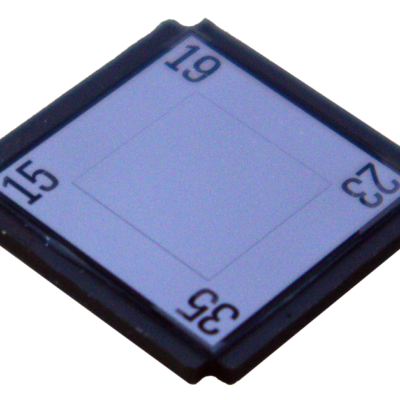
Multiple slit 15/19/23/35 µm |
SE0116 |
Chromium (55%) |
17 x 17 mm |
400 – 700 nm |
Slits 15, 19, 23, 35μm |
|
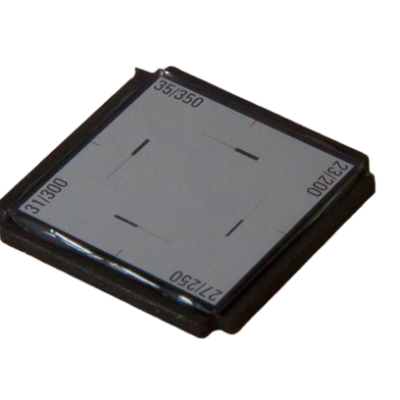
Photométric slit 23/27/31/35 µm |
SE0194 |
Chromium (55%) |
17 x 17 mm |
400 – 700 nm |
23/200, 27/250, 31/300, 35/350μm |
|
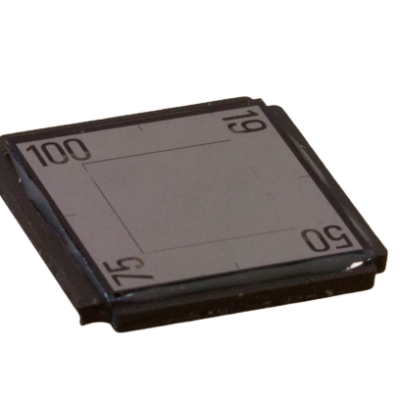
Wide slit 19/50/75/100 µm |
SE0122 |
Chromium (55%) |
17 x 17 mm |
400 – 700 nm |
Hole 19μm + slits 50, 75, 100 μm |
|
LISA slit holder |
SE0193 |
To add for all optional slits |
Recommended guiding cameras
Recommended cameras: technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Included |
Acc. type |
Cooled
|
Comment |
Camera QHY174-M GPS |
EL0253 |
Guiding camera |
yes |
The high-level solution for tracking faint targets (cooling allows > 30s exposure times) |
|
Camera ASI174 mini |
EL0244 |
Guiding camera |
No |
LISA’s “standard” guiding camera (with NO cooling). |
Recommended acquisition cameras
Recommended cameras: technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Included |
Acc. type |
Cooled
|
Comment |
Caméra ASI 533 MM Pro |
EL0327 |
Science camera |
yes |
Other accessories
Other accessories: technical specifications
Description |
Shelyak ref. |
Included |
Acc. type |
Comment |
12V/7A power supply + 4-way cable |
SE0133 |
Power supply |
12V power supply (7A), to power several accessories (cameras, lamps, etc.). Supplied with 5m silicone cable and 4 connectors (2x 2.5 mm and 2x 2.1 mm) |
|
Spare lamp for flats |
EL0116 |
Spare lamps |
Halogen lamp |
|
Argon-Neon lamps |
SE0148 |
Spare lamps |
Spare calibration lamp (Argon & Neon). Requires the calibration module. |
|
SPOX module short cable |
ES0015 |
Other add-on modules |
SPOX module for flat and calibration lamps remote control. Must be used with calibration module (SE0103). Version with short cable (80cm), if the SPOX module is installed onto the telescope. |
|
SPOX module long cable |
ES0014 |
Other add-on modules |
SPOX module for flat and calibration lamps remote control. Must be used with calibration module (SE0103). Version with long cable (5m), if the SPOX module is installed beside the telescope (on a table for instance). |
|
0.63x SCT F/6.3 focal reducer |
EL0110 |
Other add-on modules |
Focal reducer for an SCT (F/10) telescope. Changes the F-ratio from F/10 to F/6.3. |
All about the LISA spectroscope:
Description
A high-luminosity instrument
The LISA spectroscope is dedicated to the spectroscopy of faint objects such as comets, novae, supernovae, faint variable stars, the redshift of distant galaxies or quasars, or the confirmation of planetary nebulae. Its optical design has been specially studied for the observation of this type of object, with custom-made optics. Its calibration module (optional) enables easy calibration using an Argon/neon lamp, providing a large number of emission lines over the entire LISA spectral range. The same module is equipped with a tungsten lamp for flats.
A wide spectral range
With a resolving power of R = 1,000 with a 23 µm slit, its spectral range covers the entire visible range between 400 and 700 nm, and even extends into the near UV and near IR.
Example of a raw spectrum on BD+59 2829, a Be star of magnitude V=9.9 obtained with a LISA
Aperture
The LISA’s F/5 aperture makes it particularly well suited to faint objects, and it can be installed on telescopes or scopes natively f/5, but also on any type of Schmidt Cassegrain or Ritchey Chretien telescope using a focal reducer to bring the native focal length of this type of telescope, generally f/10 or f/8, down to a focal length close to 5.
Guiding system
Thanks to its mirror slit, the Lisa accurately positions and holds the target in the slit. A guiding camera (not supplied) enables the telescope’s movements to be controlled (autoguiding), ensuring optimum observation.
Field of the LISA autoguider with the slit positioned vertically, on a Seyfert galaxy
Interchangeable slit
The interchangeable slit supplied as standard (15-19-23-35µm) makes it possible to adapt the instrument to any observational situation, giving priority to resolution or brightness if required. Other slits are also available as options (wide slits, photometric slits), to further extend the possibilities.
Mechanical interfaces
The LISA is supplied as standard with a 2″ nosepiece. The nosepiece can be removed to access an T-mount female thread (M42x0.75mm thread). For mounting on a classic Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope (2″ external thread), you’ll need the BA0027 variable T-adapter.
The interface with the acquisition camera is also a T-mount thread (M42x0.75mm) with a 54.9 mm backfocus, while the guiding camera port is C-mount with a 17.5 mm backfocus.
For ATIK cameras, you need a 13mm long ring (13mm mechanical backfocus), supplied with the LISA. We offer a wide choice of adapter rings in our accessories catalog.
Going even further with LISA
In addition to the astrophysical knowledge that LISA can provide, it is also a tool for collaboration between amateur and professional astronomers: study of nova, supernova, comets, symbiotic stars, confirmation of planetary nebulae… Numerous scientific publications have been produced on the basis of LISA observations. like this one.
– ATEL Observation Ha in SS433
– Optical Spectroscopy of Classical Nova ASASSN-16ig (Nova Sgr 2016 no. 2)
– Monitoring of the slow classical nova Sct 2017
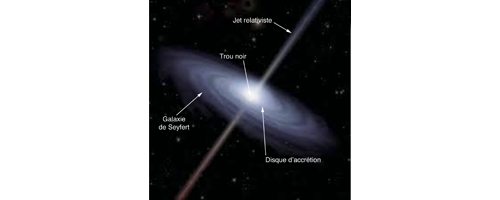
LISA spectrum of a Seyfert galaxy (z=0.061) of magnitude V=15.2
The support of a large community
LISA is used all over the world, and you can find many examples of its use and advice on the spectro-L discussion list or on the spectroscopy forum: ARAS
Specifications
- Collimator F=130mm F/5
- High efficiency thanks to internal focus reducer
- Resolution power R ~1000 with a 23 µm slit
- Grating 300 tr/mm blazed à 500nm
- Visible domain (400-700nm)
- Slit 15/19/23/35µm
- Slit length : 4 mm
- Weight: 1.4 kg (w/o caméra)
- Telescope Interface T-mount (M42*0.75), backfocus 41mm
- Science camera interface, T mount, M42*0.75, backfocus 54.9 mm
- Guiding camera interface, C-mount, backfocus 17.5 mm
Composition
- LISA Spectroscope
- Interchangeable slit : 15, 19, 23, 35μm
- Adapter for 13mm backfocus camera
Documents
- User manual.
- Dimensions
- Live observations with a LISA (online workshop)
Applications
- Calculating the redshift of distant galaxies and quasars
- Confirmation of Planetary Nebula candidates
- Spectra of faint Be stars
- Studies of star spectral classes
- Spectra of faint objects (Novae, Supernovae, Comets)
Retour d’expérience d’utilisateurs :
- First light with a LISA by Christian: Buil:http://astrosurf.com/buil/lisa3/test.htm
- First lights with a LISA by François Teyssier: http://www.astronomie-amateur.fr/Lisa.html
- First steps with a LISA (David Boyd): http://www.britastro.org/vss/First%20steps%20in%20Spectroscopy.pdf
- Confirmations of planetary nebulae (O. Garde – P. Le Dû) :
Report on mission to St-Véran observatory : http://o.garde.free.fr/RapportMissionCALAI-2016BD.pdf Mission report to C2PU Calern : http://o.garde.free.fr/RapportMissionCalern2017.pdf
- Observation with a LISA by Christian Buil: http://astrosurf.com/buil/lisa6/obs.htm
- A LISA on the T1M at Pic du Midi: http://astrosurf.com/buil/lisa4/pic_du_midi.htm
- Comet C/2009 P1 (Garradd): http://astrosurf.com/buil/garradd/obs.htm
- Herbig Ae/Be Z CMa (several spectrographs): http://astrosurf.com/aras/surveys/prestars/zcma/zcma.html
- Symbiothic star V407 Cyg: ARAS: http://astrosurf.com/aras/V407Cyg/v407cyg.htm
F. Teyssier: http://www.astronomie-amateur.fr/feuilles/Spectroscopie/SyS/V407%20Cyg.html
- Symbiothique star CI Cyg : ARAS: http://www.astrosurf.com/aras/CICyg/CI_Cyg.html
C. Buil: http://astrosurf.com/buil/cicyg/obs.htm
F. Teyssier article: http://www.astronomie-amateur.fr/Documents%20Spectro/ej143.pdf
- Very short-term temporal evolution of the cataclysmic variable DQ Her (nova Herculis 1934): http://astrosurf.com/buil/forum/dqher_poster.png
- Recurrent Nova T pyxidis (several spectrographs): http://astrosurf.com/aras/surveys/novae/tpyx/tpyx.htm
- Supernovae 2011: http://astrosurf.com/buil/supernovae/2011/obs.htm
- SN2011dh in M51 (several spectrographes): http://astrosurf.com/aras/surveys/supernovae/sn2011dh/obs.htm
- NGC7331: http://astrosurf.com/buil/forum/ngc7331_poster.png
- A somewhat subtle observation by Christian Buil and Valérie Desnoux, but also a bit mythical, which highlights the rotation of a galaxy on itself (NGC 7331). The power and good shape of the T60 (Pic du Midi) combined with the LISA spectroscope make an exceptional pair.
- Quintet of Stephan: http://astrosurf.com/buil/forum/stephan_poster.png
- Spectroscopic observations of Nova Delphini 2013 [= V339 Delphini], David Boyd, Journal of British Astronomical Association 123, 5, 2013, p 302 : http://www.britastro.org/vss/Spectral%20evolution%20of%20Nova%20Delphini%202013%20(V339%20Del).pdf
Software
Articles related to the LISA spectroscope :
How to measure the redshift of a galaxy ?
Comment mesurer le redshift d’une galaxie lointaine avec un spectrographe basse résolution.